Sustainable Coastal Ecosystem (CASCE) Project, Bangladesh.
Bangladesh is one of the most climate vulnerable countries in the world. The country is frequently subjected to cyclones, floods, and storm surges due to the adverse impact of climate change. Around 35 million people who are living in 19 coastal districts of the country are in the highest level of climate risks. Experts suspected that due to global warming, 10-15% Bangladesh’s land could be inundated by 2050, resulting in over 25 million climate refugees from the coastal districts.
Coastal communities in Bangladesh are highly resource poor and extremely vulnerable to climate change impacts. Livelihoods of coastal people hinge on small holding agriculture, fisheries and livestock farms where low income and poor diversity in options further increase their vulnerability.
Objective
The project is aimed at reducing climate vulnerability of local communities through participatory planning, community-based management, integration of climate resilient livelihoods and diversification of species in afforestation and reforestation carbon project.
Project Overview:
An innovative livelihood approach for reducing vulnerability to climate change in the coastal areas in Bangladesh.
Project Name: Community Lead Agroforestry for Sustainable Coastal Ecosystem (CASCE) Project, Bangladesh.
Project Model: Forest, Fruit, Fish & Vegetables (3FV)
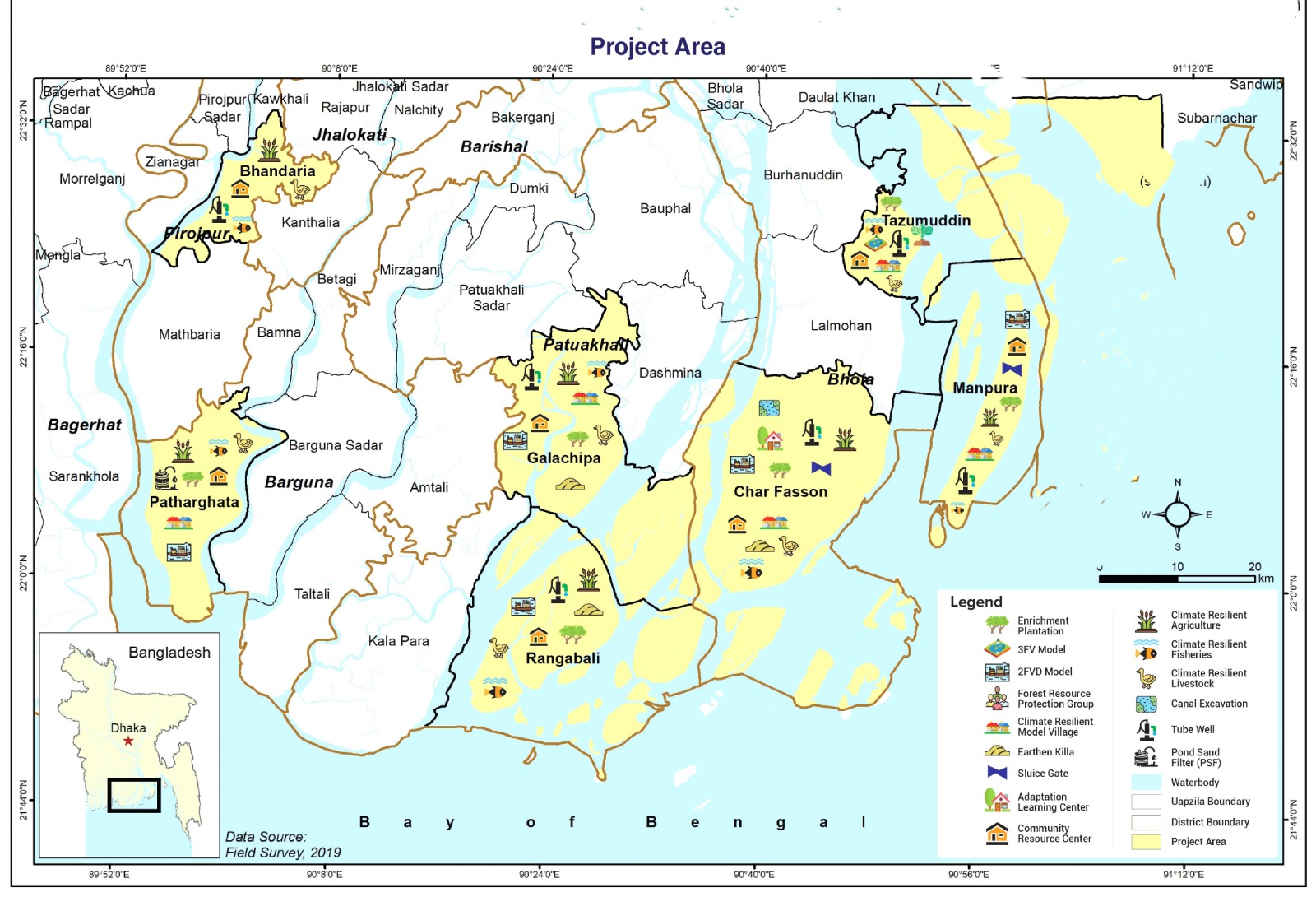
Project Area: Barguna (7 Upazila), Patuakhali ( 7 Upazila), Bhola (6 Upazila)
Bangladesh Map
Project Area
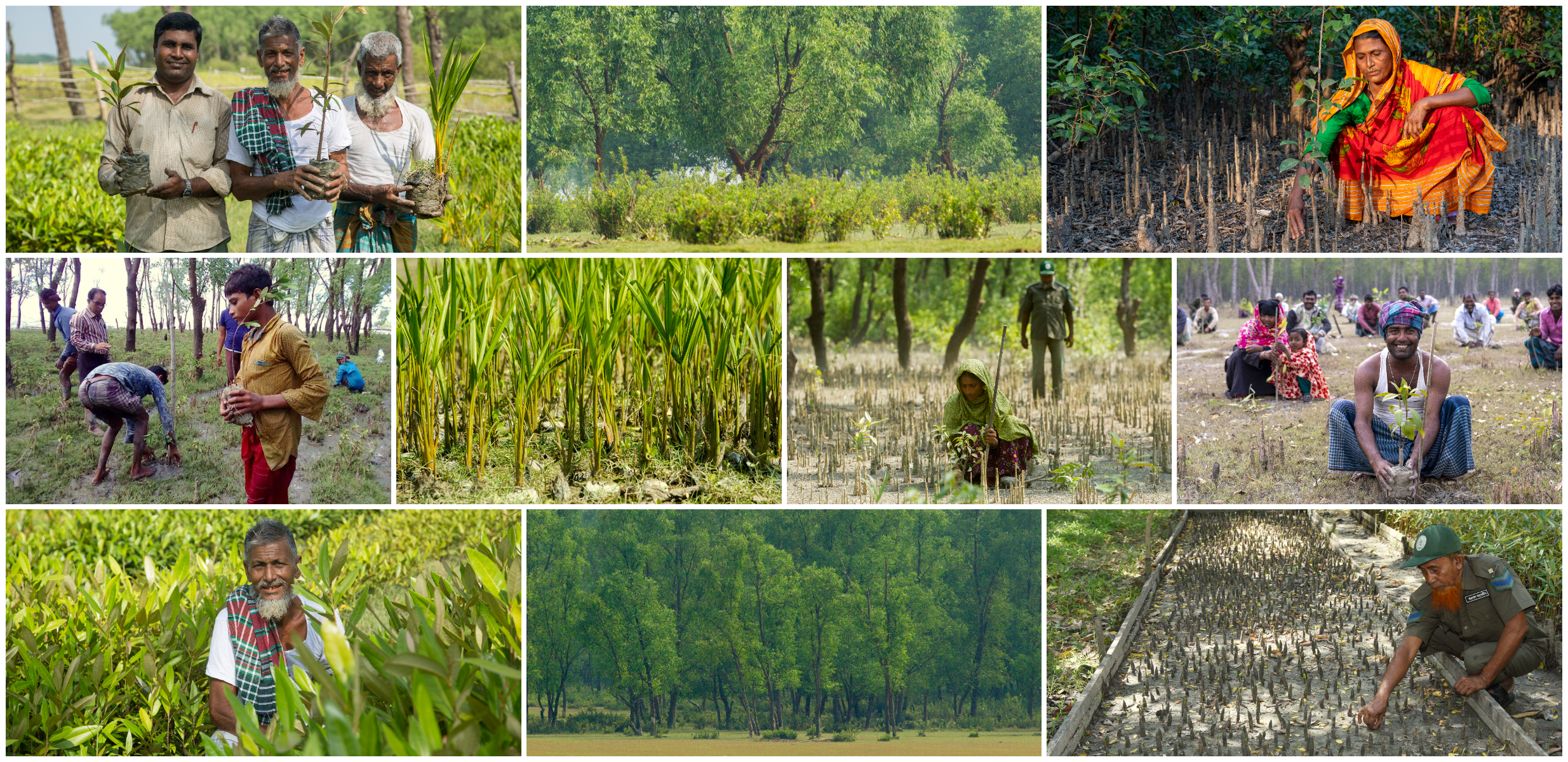


The model offers income to landless vulnerable poor households in short, medium and long terms thorough integrated options based on forest, agricultural, fisheries and livestock. The Dyke of a 3FV model is used for growing a wide variety of timber and fruit trees, and vegetable while the ditch is used for fish culture. Thus, 3FV model reduces climate risks by ensuring year-round income and food security. The continued flow of resources and income generated from 3FV model enhances resilience of poor coastal people and reduces their dependency of coastal forests.
3FV model converts less productive coastal land into more productive lands. Moreover, as part of the 3FV model a patch of mangrove species is planted along the coastal line adjacent to the model which protects land and human settlement against cyclone, storm surges and strong winds.
The ‘Forest, Fruit, Fish and Vegetable’ (3FV) model is a successful community-based adaptation option for coastal communities in Bangladesh. 3FV model has opened a new window of opportunity for rational coastal land use in Bangladesh by empowering coastal communities with land rights and introducing innovative land use technologies to generate large scale social and ecological benefits for adaptation
Tree Plantation
8 million
Households
350,000
Directly Benefit
1 million people
Job Creation
200 Jobs
Rewilding

12 Species

Any question or remarks? Just write us a
message!
